For cash overage in petty cash, we can make the journal entry with the debit of the expense accounts and the credit of the cash over and short account and the cash account when we replenish the petty cash. For other types of businesses, the cash shortage usually happens when dealing with petty cash. For example, the petty cash custodian may sometimes find themselves having less cash on hand as a result of the total cash plus receipts does not add up to the total amount of the established petty cash fund.
What is the Journal Entry to Record a Cash Overage?

The journal entry to record this sale would debit cash for $101, credit sales for $100, and credit cash over short for one-dollar. Most retailers’ accounting systems have a cash over short account setup because they generally deal with cash sales everyday. In accounting, cash over and short journal entry is usually made when the company replenishes its petty cash fund.
Bookkeeping
- In this journal entry, we credit the sales revenue because in the retail business the cash shortage usually happens due to us failing to keep the accurate records that are related to sales revenue.
- I rang up a $95 pair of yoga pants correctly for $95, but I miscounted the cash I received for the pants.
- This classification helps in identifying whether these discrepancies are one-off incidents or part of a recurring pattern.
- These errors cause the cash in the fund to be more or less than the amount of the fund less the total vouchers.
- Surprise cash counts add an additional layer of security by preventing employees from preparing for the count, which can help to uncover any discrepancies that might otherwise be concealed.
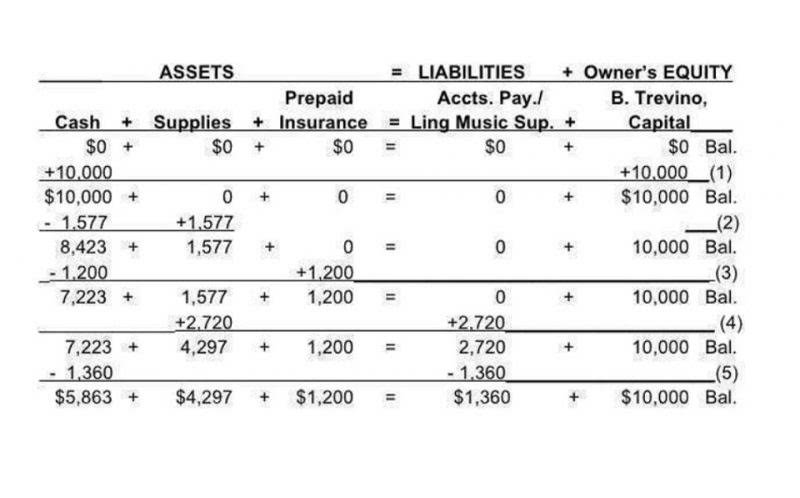
In this case, when we replenish the petty cash, we just need to refill $77 ($100 – $23) as we still have $23 remaining in petty cash. Double Entry Bookkeeping is here to provide you with free online information to help you learn and understand bookkeeping and introductory accounting. This account is used to record both increases and decreases to profits resulting from errors. Generally, the amounts in the account Cash Short and Over are so small that the account balance will be included with other insignificant amounts reported on the income statement as Other Expenses. This example demonstrates how a decline in the euro’s value relative to the dollar can result in a profitable short trade. As you think back on this system, note that there are several internal controls in place, most notably segregation of duties, assignment of responsibility, and a reconciliation (monitoring) process.
- Opposite to the cash shortage, cash overage occurs when the cash we have on hand at the end of the day is more than the cash sales.
- Human error is a frequent contributor, with cashiers sometimes entering incorrect amounts into registers or giving improper change.
- The cash overage or cash shortage may also come from the sale and other expense transactions too.
- This is probably due to there have been many transactions for our retail business as it is near holiday resulting in errors in our calculation.
- To realise your profit or loss, you will need to close your position.
- A firm should note instances of cash variances in a single, easily accessible account.
Investigating Cash Discrepancies

Cash shortage usually happens when the actual cash on hand received from sales is less than the total amount in sales receipts for the retail business. For other types of businesses, it usually occurs when the cash on hand, left after petty cash expenses, is less than the total amount in petty cash expenses receipts. The physical transactions for petty cash, cash short and over need recording with the appropriate journal entries. Here, you create a new journal entry in your accounting journal and debit, or increase, cash short and over account each expense account by the amount of cash used by your vouchers. In the example, debit the office supplies expense account for $300, and debit the transportation expense account for $140.
Over and Short: Definition and What It Means in Accounting
A series of cash overs and shorts may be a sign of theft or other problems in the company. The cash over and short is recorded on debit when there is a shortage. In contrast, the cash over and short is QuickBooks recorded on credit when there is overage.